4 Ways to Free-Up disk space. (Without destroying your computer.)
1. Shadow Copies
Shadow copies were introduced back in WinXP days. They were geared towards big companies that had lots of important information. If someone deleted or modified a file and you needed the original copy back, shadow copies could get it for you.
It’s not as idealistic as it sounds. Shadow copying just makes periodic copies of files that you enable it on. So, instead of having 1 40KB word document, you have 10, from the past 10 weeks. Obviously, this method can take up a lot of disk space.
Most of us don’t really care about our data. And when we do, we’re smart enough to back it up somewhere else. But Microsoft has enabled shadow-copies by default with Windows Vista and Windows 7.
So, to fix this problem, you can limit the amount of space that Windows uses for Shadow Copying (also known as VSS).
>Resizing Shadow Copy Space
(This procedure only works on Vista and Win7.)
1. Open the start menu and type in Command Prompt. Right click the Command Prompt icon and click Run as Administrator. If a User Account Control dialog pops up, allow the Command Prompt to run.
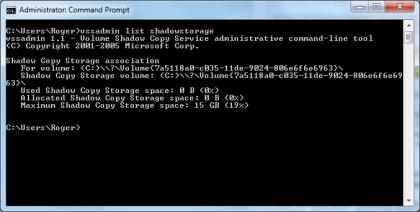
2. In the elevated command prompt, type in vssadmin list shadowstorage.
You should get some results that look like this:
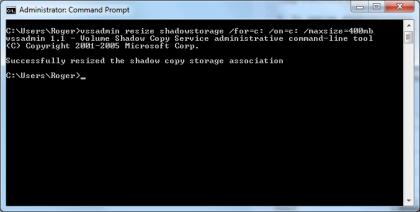
3. To resize shadowstorages, type in vssadmin resize shadowstorage /for=c: /on=c: /maxsize=400mb
But before you do that, make sure that the drive letters match. I recommend resizing it to 400Megabytes, but this is really up to you.
After you press enter, VSSAdmin should tell you that everything went OK.
Check your diskspace now. Did it go down far enough? If not, keep reading.
2. System Restore
One of the most useless features about Windows is System Restore. Most of the time, it doesn’t work. When it does work, it doesn’t do what you want it to. And the worst part is, it can take up a ton of disk space on your computer.
Just in case, Windows doesn’t let you delete the most recent restore point on your computer. However, you’re free to delete the hundreds of points that came before that.
>Resizing Shadow Copy Space
(This procedure only works on Windows XP, Vista and Win7.)
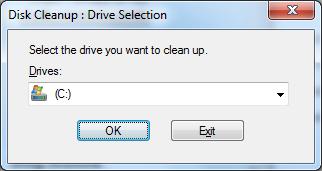
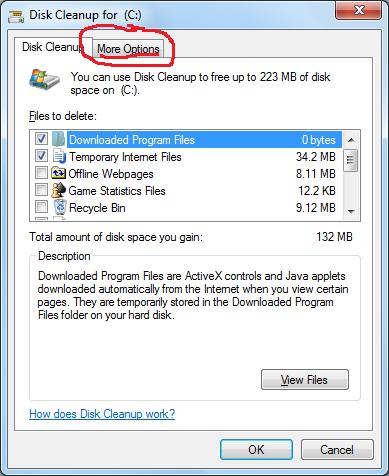
1. Open the Start Menu and type in Disk Cleanup. (In Windows XP, go to All Programs > Accessories > System Tools > Disk Cleanup)
2. Select the disk that you want to clean. (This should be the C drive.)
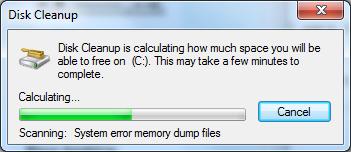
3. Disk Cleanup will start scanning. Just wait. :) It shouldn’t take too long.
4. You’ll get this fancy window with lots of options to free up space on your disk. But that’s not important. The important part is that other tab at the top. So, click the tab that says More Options.
5. In the bottom half of this new tab, you can choose to delete old Restore Points and Shadow Copies.
So, click that button, and watch them be deleted.
(Deleting Shadow Copies from this panel only removes them temporarily. In a few weeks, they’ll be back to start clogging up your computer again. To get rid of Shadow Copies permanently, use the method that I explained in part 1.)
6. Did that free up enough disk space? You’re welcome to try the options on the first pane of Disk Cleanup, but those aren’t as effective.
3. Paging File
If you have less than 2GB of RAM on your computer, skip this part. It won’t free up that disk space. Paging files usually take up 1.5x the amount of RAM that you have on your computer.
A long time ago, harddrive Megabytes were dirt cheap compared to Physical Memory Megabytes. (I mean a really long time ago. I mean, they were still using megabytes ._.)
So, Microsoft thought up of an idea to save their customers money. Why not use harddrives as RAM? (Btw, this idea is a.k.a. Paging Files or Virtual Memory) Well, first of all, Harddrives are hundreds of times slower than RAM.
But this post isn’t titled "How to speed up your computer". No. The point is, using your harddrive as RAM can take up lots of harddrive space. If you feel like you have enough RAM on your computer, you can lower the amount of space that is used for paging files.
>Changing the size of the Paging File
1. Right click my computer and press "Properties".
Windows XP Users:
2. Go to the advanced tab.
Windows Vista and Windows 7 Users:
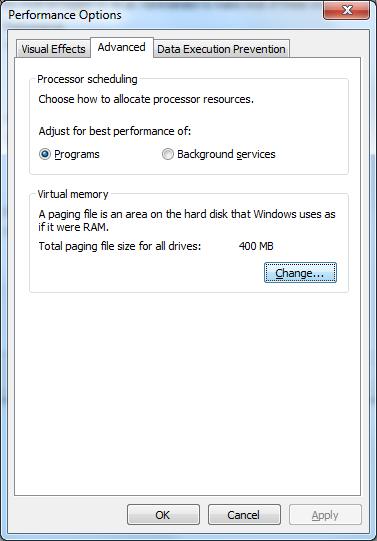
2. There’s a pane on the left side of the window. Click where it says "Advanced System Settings".
3. Under the Performance section, click "Settings".
4. Go to the Advanced tab and under "Virtual Memory", click Change.
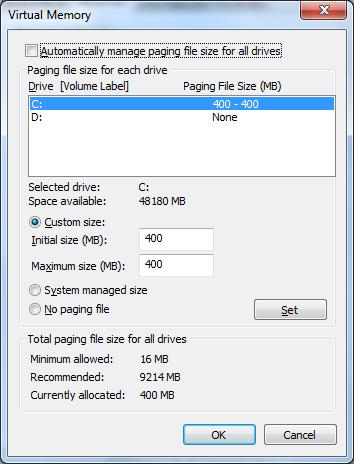
5. Here, you can set the amount of disk space that is used for Virtual Memory. Use the "Custom Size" option and enter the desired number in MegaBytes. I’m using 400MB on my C:\ Drive for Virtual Memory.
6. Don’t forget to restart your computer at the end!
7. If those three methods didn’t do enough to free up disk space, try this one last one:
4. Hibernation
Yeah. Hibernation. Like bears right?
No, not really. Hibernation saves everything on your RAM to your harddrive so that your computer starts up like BAM the next time you turn it on. It’s a good concept, but it also takes up a lot of disk space.
To disable hibernation, do the following steps:
>Disabling Hibernation
(This only works with Windows XP)
1. Go to Control Panels > Power Options.
2. In the Hibernation tab, uncheck the "Enable Hibernation" checkbox.
Disabling hibernation in Windows 7 and Vista is more complicated and I don’t recommend it if you don’t know what you’re doing. (Btw, click the link at the beginning of this paragraph to learn how to disable hibernation in Vista/7.)
If none of these methods have satisfied your needs, go buy a new Harddrive. Preferably, a bigger one. Alright?
-Roger